> Water
> Reducing water consumption through product innovation
> The Cleaner Ganges project
Topics addressed in this section:
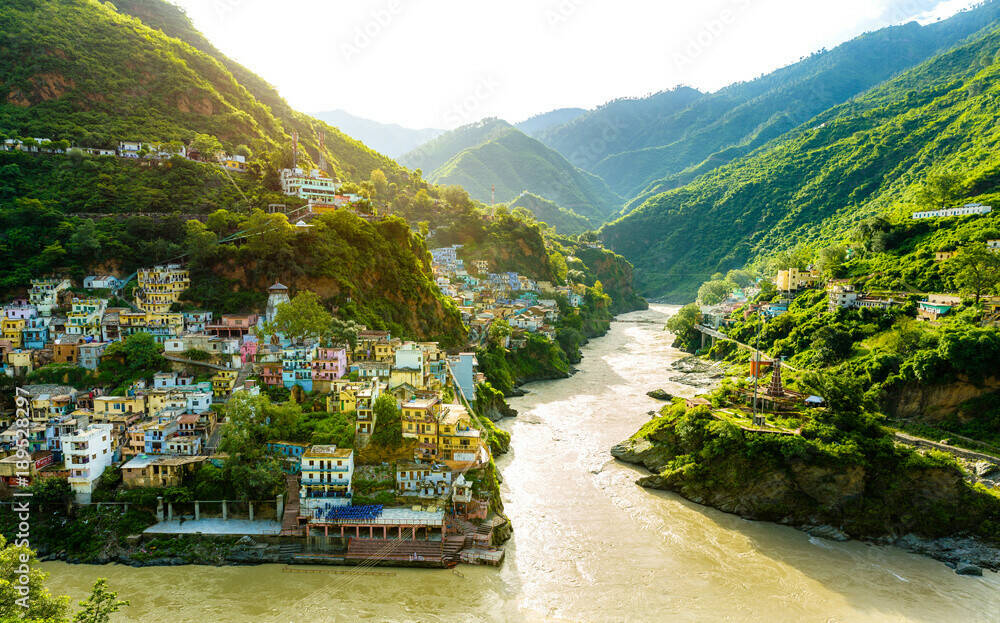
The Kanpur leather cluster is one of India’s most important areas for leather production, but the wastewater it produces is a pressing issue. To address this, in 2017 Stahl entered into a five-year public-private partnership to reduce the environmental impact of leather production in Kanpur. Partners included Solidaridad, PUM Netherlands, the Ganges Pollution Control Unit, The Sustainable Water Fund (FDW), and the Dutch Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
Stahl's approach was twofold. We introduced an innovative “pickle-free” tanning process that reduced the amount of wastewater produced by 40%. We also shared our expertise through the Stahl Campus® program we established at our Center of Excellence in Kanpur, which focused on more sustainable leather technologies. In 2022, the Kanpur project was extended by one year due to COVID-related closures and will now run until the end of 2023.
Having proven the concept, we plan to roll out the pickle-free process in other leather clusters, and a similar public-private partnership with Solidaridad was launched in Kolkata in 2022. This three-year project will also focus on reducing the environmental impact of the growing leather manufacturing cluster in the region.
Ganges project


Back to overview

Scroll
down
Water is a critical resource in the manufacture of our products, and Stahl uses it in a variety of ways. Clean water is also essential for a thriving environment and for human health and well-being. At Stahl, we consider the impact our water consumption can have on our local communities and the environment. We devote significant resources to researching how we can further reduce our water consumption, introduce more water-based products, improve the quality of our effluent, and help our customers and other value chain partners to conserve water and reduce water pollution.
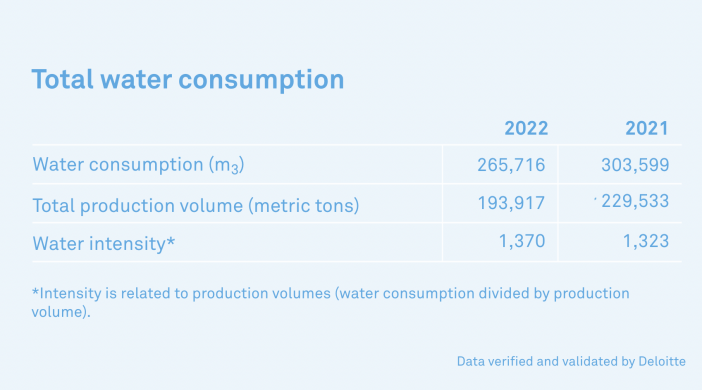
We use water from municipalities (public water) and groundwater in our operations. Our manufacturing sites use water for making our products, cleaning tanks and pipes, and for heating and cooling. We also use water in our offices and laboratories. In 2022, our water use decreased due to lower production volumes. Our water intensity (water used per metric ton of product manufactured) was stable.

Water use at the Palazzolo site (Italy)
At Stahl’s Palazzolo manufacturing site in Italy, we are taking steps to help the local community maintain a low groundwater level. Cooling water at the site is taken temporarily (i.e., not used) from a ground well, completely separated from water used for production, and discharged into the adjacent river. This specific use of water is approved by the local authorities and follows their strict guidelines.

Data verified and validated by Deloitte
Advancing new water-based technology
Over the past 20 years, water-based technology has steadily replaced petrochemical solvent-based products in Stahl’s coating and finish portfolio. Water-based products typically have a much lower carbon footprint than their (fossil) solvent-based equivalents. In 2022, 57% of our sales revenue came from water-based products (defined as containing >50% water and <15% co-solvent). Our 2022 life cycle assessments show a significant reduction in the carbon footprint of water-based products compared to solvent-based equivalents.
In addition to reducing our own water consumption, Stahl develops solutions to help our customers and other value chain partners limit their water consumption and maximize wastewater recycling in their own production processes. For example, Stahl’s EasyWhite Tan® metal-free tanning solution enables leather tanneries to reduce their water consumption during the tanning process. Wastewater from Stahl EasyWhite Tan® tanning can also be captured and reused in the liming process. This helps reduce both water consumption and effluent discharge.
Back
to top

Back to overview

Ganges project
The Kanpur leather cluster is one of India’s most important areas for leather production, but the wastewater it produces is a pressing issue. To address this, in 2017 Stahl entered into a five-year public-private partnership to reduce the environmental impact of leather production in Kanpur. Partners included Solidaridad, PUM Netherlands, the Ganges Pollution Control Unit, The Sustainable Water Fund (FDW), and the Dutch Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
Stahl's approach was twofold. We introduced an innovative “pickle-free” tanning process that reduced the amount of wastewater produced by 40%. We also shared our expertise through the Stahl Campus® program we established at our Center of Excellence in Kanpur, which focused on more sustainable leather technologies. In 2022, the Kanpur project was extended by one year due to COVID-related closures and will now run until the end of 2023.
Having proven the concept, we plan to roll out the pickle-free process in other leather clusters, and a similar public-private partnership with Solidaridad was launched in Kolkata in 2022. This three-year project will also focus on reducing the environmental impact of the growing leather manufacturing cluster in the region.
Advancing new water-based technology
Over the past 20 years, water-based technology has steadily replaced petrochemical solvent-based products in Stahl’s coating and finish portfolio. Water-based products typically have a much lower carbon footprint than their (fossil) solvent-based equivalents. In 2022, 57% of our sales revenue came from water-based products (defined as containing >50% water and <15% co-solvent). Our 2022 life cycle assessments show a significant reduction in the carbon footprint of water-based products compared to solvent-based equivalents.
In addition to reducing our own water consumption, Stahl develops solutions to help our customers and other value chain partners limit their water consumption and maximize wastewater recycling in their own production processes. For example, Stahl’s EasyWhite Tan® metal-free tanning solution enables leather tanneries to reduce their water consumption during the tanning process. Wastewater from Stahl EasyWhite Tan® tanning can also be captured and reused in the liming process. This helps reduce both water consumption and effluent discharge.
Water use at the Palazzolo site (Italy)
At Stahl’s Palazzolo manufacturing site in Italy, we are taking steps to help the local community maintain a low groundwater level. Cooling water at the site is taken temporarily (i.e., not used) from a ground well, completely separated from water used for production, and discharged into the adjacent river. This specific use of water is approved by the local authorities and follows their strict guidelines.

Back
to top
Water is a critical resource in the manufacture of our products, and Stahl uses it in a variety of ways. Clean water is also essential for a thriving environment and for human health and well-being. At Stahl, we consider the impact our water consumption can have on our local communities and the environment. We devote significant resources to researching how we can further reduce our water consumption, introduce more water-based products, improve the quality of our effluent, and help our customers and other value chain partners to conserve water and reduce water pollution.
We use water from municipalities (public water) and groundwater in our operations. Our manufacturing sites use water for making our products, cleaning tanks and pipes, and for heating and cooling. We also use water in our offices and laboratories. In 2022, our water use decreased due to lower production volumes. Our water intensity (water used per metric ton of product manufactured) was stable.